Author: Fuyuan Zheng abc1, Xiujuan Chen cd1, Yueming Li e, Shouyin Xu c, Yunhui Li ab, Qingming Xu b, Jianwei Zhu b, Yumin Liu b, Guorui Zhao c
Journal: Journal of Alloys and Compounds
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2025.182663
Abstract / 摘要
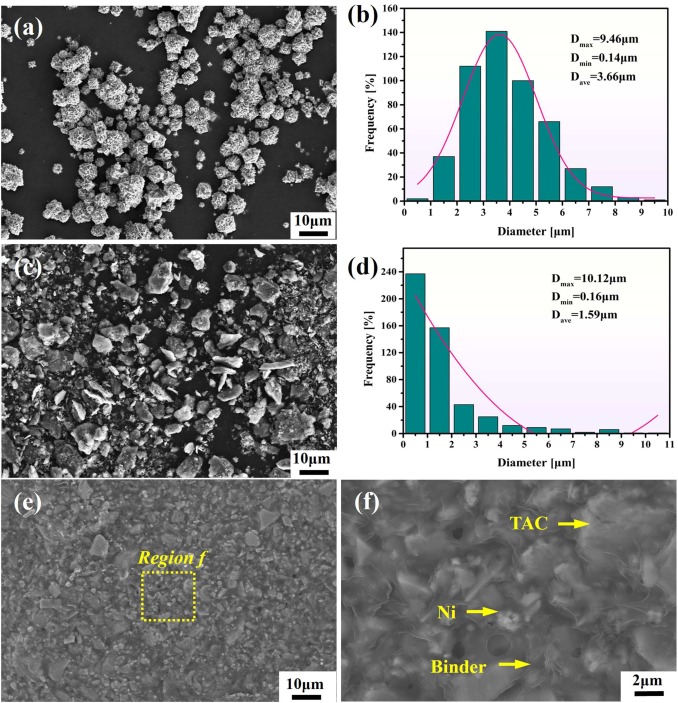
Additive manufacturing of ceramic matrix composites has significant potential for industrial applications, particularly in producing parts with highly customized production of specific structural and functional characteristics of parts, while its fabrication still faces many challenges. In this study, a novel technology, Powder Extrusion Printing (PEP) combined with in-situ reaction, was successfully employed to prepare the high performance of TiC matrix composite cutting tools using Ti3AlC2 and Ni as raw materials. The formation of TiC and NiAl was observed in the sintered sample. The crystallographic orientation relationships in TiC-Ti2AlC-NiAl interfaces were also determined, as follows: TiC [11−2]∥Ti2AlC [1−100]∥NiAl [-110], TiC (111)∥Ti2AlC (000−2)∥NiAl (110). As the load increases from 0.3 kg to 10 kg, the Vickers hardness (HV) gradually decreases from 12.51 ± 0.40 GPa to 11.12 ± 0.10 GPa. The three-point bending strength, fracture toughness (KIC) and compressive strength of the sintered samples were 528.30 ± 63 MPa, 6.31 ± 0.17 MPa·m1/2 and 1211 ± 165 MPa, respectively. Thus, this technology exhibits excellent application potential in the fabrication of ceramic-based composites with complex shapes.
Keywords / 关键词
Additive manufacturing; Powder extrusion printing (PEP); TiC matrix composites; In-situ reaction