Author: Xijie Zhang abc1, Hao Zhang c1, Yueming Li d, Yunhui Li ab, Jianwei Zhu ab, Yuming Liu ab, Qingming Xu ab, Guorui Zhao c
Journal: Separation and Purification Technology
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2025.134258
Abstract / 摘要
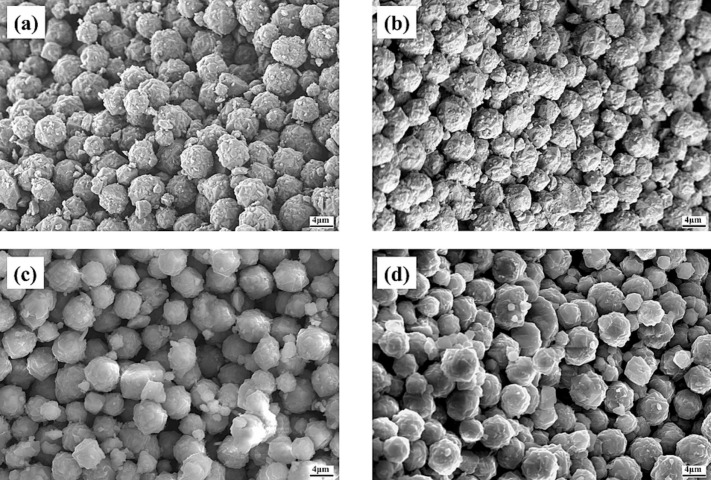
In this study, a strategy for preparing monolithic Li-LSX molecular sieves using the PEP additive manufacturing technology was proposed, and the impact of various thermal debinding temperatures on the mechanical strength, porosity, and gas adsorption performance, particularly for nitrogen–oxygen separation were investigated. Orthogonal experimental analysis showed that layer height had the greatest effect on relative density and dimensional accuracy. The optimal optimized parameters were a layer height of 0.2 mm, a flow rate of 22 %, and a print speed of 25 mm/s. XRD and FTIR spectroscopy analyses confirmed that the Li-LSX phase composition remained unchanged during printing and debinding. After debinding treatment at 200°C, its compressive strength remained at 0.5 MPa. Moreover, the N2/O2 separation performance of monolithic Li-LSX molecular sieves remained consistent at consecutive adsorption cycles, with the separation ratios Sa and Sb stabilizing at approximately 6 and 10, respectively.
Keywords / 关键词
Li-LSX molecular sieve; Nitrogen and oxygen separation; Powder extrusion printing; Additive manufacturing